Comprehensive Guide for Algae-based CO2 Capture
Thousands of CO2 emitting power plants and industries face a costly problem - reduce their CO2 emissions or pay penalties. What if these companies and power plants could use algae to absorb the CO2 and generate biofuels in return? This is precisely what companies and power plants around the world are beginning to explore. This comprehensive report will provide you with rich and practical insights and data for you to start quickly working on this domain either as a researcher or as an industry. 
|
 | ||||||||

Price - US$ 1000,
Pages - 677,
Last Updated - March 2017
About Oilgae
Oilgae is the premier resource for the global algae energy industry. Started in 2006 with a dedicated focus on algae energy, Oilgae today serves as a crucial platform and opinion-leader for this industry.
The Oilgae team is frequently interviewed by leading world media and frequently presents at seminars and conferences. Some of the media that Oilgae has been mentioned in are: WorldChanging (Columbia University), BBC, Salon Magazine, Los Angeles Times, New York Times, Wired, India Times and more.
Oilgae today is so synonymous with algae energy that many people worldwide use Oilgae as the word to refer to oil from algae!
Comprehensive knowledge and understanding on the following:
- Detailed information on processes & challenges of algae- based CO2 capture
- Industry & market information of algae- based CO2 capture
- Status of Current CO2 Capture and Storage (CCS) Technologies
- Latest Developments in CO2 Sequestration
Why should you buy this report
- It helps you understand all aspects of the algae energy domain and provides you key insights which will be invaluable in planning your venture.
- It includes a number of real life case studies to assist the reader in gaining a more practical perspective of the industry status.
- It has been developed with inputs from authoritative sources.
- Special emphasis is on inputs that will facilitate businesses to quickly take further steps.
- Comprises intelligence and inputs derived from many seminars and expert presentations
- Developed by Oilgae (www.Oilgae.com), the leading resource for all information for energy from algae
(Click here to view free preview report)
To download a copy of the preview to your machine , click here
Specific Questions and Challenges to Which Answers are Provided in the Report
|
Companies Involved in Algae-based CO2 Sequesteration
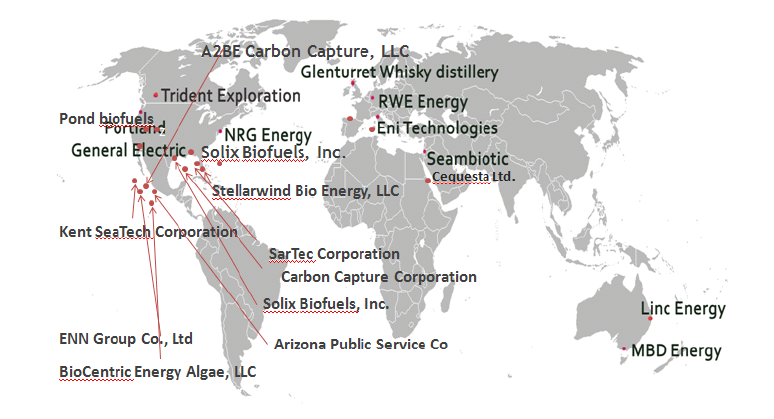
The report provides inputs on three major aspects of algae- based carbon-dioxide capture.
| Concepts of Algae-Based CO2 Capture | This section provides information on concepts of algae-based CO2 capture and algae Species suited for CO2 capture of power emissions. |
| Processes & Challenges | This section provides information on process for algae cultivation near power plants and challenges of algae-based CO2 capture. |
| Industry & Market Information | This section provides information on cost of CO2 capture using algae, companies involved in algae-based CO2 sequesteration, potential for existing companies in related industries entering algae energy domain, status of current CO2 Capture and Storage (CCS) technologies |
Potential of Algae – based CO2 Capture:
Power Plants Need to Control their CO2 Emissions
Typical coal-fired power plants emit flue gas from their stacks containing up to 13% CO2. It is estimated that power plants produce over 30% of all greenhouse gases worldwide.
There are about 50,000 power plants in the world, with 8,000 of them in the US alone!
Critical Problem 1 - These thousands of power plants need an effective solution by which they can reduce their net CO2 emissions.
Algae Love CO2, But Need Concentrated CO2 Sources
Algae, especially microalgae, just love CO2. Each ton of algae produced consumes about 1.8 T of CO2. In fact, for many millions of years, algae have been the largest consumer of CO2 (and largest emitter of oxygen) in the world. It can thus be said that all living beings on earth owe their lives to algae!Current efforts to make biofuels from algae face the problem of finding concentrated sources of CO2 as algae require much higher concentrations of CO2 than are found in the atmosphere.
Critical Problem 2 - In order to become an effective feedstock for biofuels, algae require concentrated sources of CO2.
Combine Two Critical Problems and You Get A Powerful Solution
One ton of algae biomass requires about 1.8 T of CO2; this implies that out of 10 billion T of CO2 that the power plants emit, we can get about 5.5 billion T of algae biomass.
The right strains of algae have about 30% of oil by weight. Thus, 5.5 billion T of algae will result in about 1.65 billion tons of oil.
The total world consumption of oil is about 4.2 billion T of oil every year.
The Key Advantages of CO2 Capture Using Algae are:
- Owing to the fact that high purity CO2 gas is not required for algae cultivation, flue gas containing CO2 and water can be fed directly to the photobioreactor.
- Power plants that are powered by natural gas or syngas have virtually no SO2 in the flue gas. The other polluting products such as NOx can be effectively used as nutrients for micro algae.
- Microalgae culturing yields high value commercial products that could offset the capital and the operation costs of the process, at least to some extent. In addition to biofuels, algae are also as the starting point for high-protein animal feeds, agricultural fertilizers, biopolymers / bioplastics, glycerin and more.
- Depending on the species, algae can grow in temperatures ranging from below freezing to 158oF. Thus the right strain of algae can
- The entire process is a renewable cycle.
Benefits
Business opportunities exist both for companies that are CO2 emitters as well as for external businesses such as consulting and engineering companies that are willing to work with power plants to make the algae-based CO2 sequestration and biofuels production a reality.
List of Potential Industries
In addition to being a promising future feedstock for biofuels, algae have tremendous potential for other applications, including industrial enzymes, medical therapeutics, and even animal feeds.
Though most of the companies interested in cultivation of algae for the production of biofuel feedstocks and animal nutrition product, algae can be cultivated to serve many additional commercial and industrial uses:
|
Free Sample ReportFree Download(Click here to view free preview report) |
The algae-based CO2 capture avenue thus provides the companies the opportunity to capture CO2 (and possibly earn carbon credits) while at the same time producing Biofuels.
In addition to power plants, algae can be grown on flue gases emitted from many other industrial sources as well. Examples of other industries that emit significant amounts of CO2 are:
- Cements
- Iron & Steel
- Petrochemicals
- Sugar
- Tyres
- Carbon Black
- Mining
- Aluminium
- Paper
- Inorganic Chemicals
- Fertilizers
- Breweries
A number of businesses around the world have realized the potential of algae-based CO2 capture and are taking their first steps to explore this exciting avenue.
In order to assist industries and companies that are keen on exploring the potential of using algae for CO2 capture, Oilgae has come up with the Oilgae Guide to Algae-based CO2 Capture, a comprehensive report on this topic.
The report focuses on the potential of algae-based CO2 capture, and provides critical inputs on current efforts, bottlenecks, costs and challenges facing this vital segment.
List of Contents
Section 1 – Concepts of Algae-based Co2 Capture
- Algae-based Co2 Capture
- 1.1 Introduction & Concepts
- 1.2 Composition of Power-plant Flue Gas
- 1.3 How Are Algae Grown Next to Power Plants Cost Effective?
- 1.4 Need for Algae-based Co2 Capture
- 1.5 Business Opportunities from Algae-based Co2 Capture
- 1.6 Ideal Attributes of Photosynthetic Sequesteration
- 1.7 Algae Co2 Capture Value Chain
- Algae Species Suited for CO2 Capture of Power Emissions
- 2.1 Importance of Algal Strain Selection
- 2.2 Parameters for Strain Selection
- 2.3 Algal Species Suited for CO2 Capture of Power Plant Emissions
- Process for Algae Cultivation near Power Plants.
- 3.1 Introduction
- 3.2 Methods and Processes - Overview
- 3.3 Flue Gas Collection and Preprocessing
-
- 3.3.1 Flue Gas Preprocessing
- 3.3.2 State(temperature) and Composition of Flue Gas on Collection
- 3.3.3 Cooling/Condensation
- 3.3.4 Scrubbing of Flue Gas
- 3.3.5 SOx Removal
- 3.3.6 NOx Removal
- 3.3.7 Heavy Metal Removal
- 3.3.8 Dehydration
- 3.3.9 Dust Separation
- 3.3.10 CO2 Concentration
- 3.4 Transportation of Flue Gas
- 3.5 Distribution System
- 3.6 Carbonation system
- 3.7 Open Cultivation Systems
- 3.8 Process for Algae Cultivation near Power Plants
- Challenges of Algae-based CO2 Capture
- 4.1 Concepts
- 4.2 Challenges of Algae-based Carbon-Capture
- 4.3 Research and Data for Algae-based CO2 Capture
- 4.4 Algae-based CO2 Capture - Factoids
- Cost of CO2 Capture Using Algae
- 5.1 Introduction
- 5.2 Cost for:
- 5.2.1 Separation of Carbon-dioxide from the Flue-gas
- 5.2.2 Cost for Carbon-dioxide Compression and Capture
- 5.2.3 Carbon-dioxide Storage
- 5.3 Representative Cost of Algae-based Carbon-capture
- 5.4 Costs - Reference
- Companies involved in Algae-based CO2 Sequesteration
- 6.1 Introduction
- 6.2 Companies & Profiles
- 6.3 Case Studies
- Potential for Existing Companies in Related Industries Entering Algae Energy Domain
- 7.1 Prominent CO2 Emitting Industries
- 7.2 Industries with Synergistic Benefits from Algae Energy Opportunities
- Status of Current CO2 Capture and Storage (CCS) Technologies
- 8.1 Introduction
- 8.2 Emerging Technologies in CO2 Storage
- 8.3 in CO2 Sequestration
- 8.4 Implementation Status
- Appendix
- 9.1 Algae Cultivation Coupled with CO2 from Power Plants – Q&A
- 9.2 Reference
- Energy from Algae - Introduction
- 10.1 Algae
- 10.2 Energy from Algae
- 10.3 History & Current Status of Energy from Algae
- 10.4 Algae Energy & Alternative Energy
- 10.5 Big Challenges & Big Payoffs
- 10. 6 Energy “Products” from Algae
- 10.7 Determining the Optimal “Energy Product”
- 10.8 Algae to Energy – Summary of Processes for Each Energy Product
- 10.9 Trends & Future of Energy from Algae
- 10.10 Factoids
- Algal Strain Selection
- 11.1 Importance of Algal Strain Selection
- 11.2 Parameters for Strain Selection
- 11.3 Strains with High Oil Content & Suitable for Mass Production
- 11.4 Strains with High Carbohydrate Content
- 11.5 Strains – Factoids
- 11.6 Challenges & Efforts
- Algae Cultivation
- 12.1 Introduction & Concepts
- 12.2 Algaculture
- 12.3 Infrastructure for Algae Cultivation
- 12.4 Different Methods of Cultivation
- 12.5 Algae Cultivation – Factoids
- 12.6 Worldwide Locations with Algae Farms & Algae Cultivation
- 12.7 Algae Cultivation Challenges & Efforts
- 12.8 Research & Publications
- 12.9 Reference
- Algae Grown in Open Ponds, Closed Ponds & Photobioreactor
- 13.1 Introduction
- 13.2 Open-Ponds / Raceway-Type Ponds and Lakes
- 13.3 Details on Raceway Ponds
- 13.4 Algal Cultivation in Open Ponds – Companies and Universities
- 13.5 Challenges in Open Pond Algae Cultivation
- 13.6 Algae Cultivation in Open Ponds – Q&A
- 13.7 Algae Grown in Closed Ponds
- 13.8 Algae Cultivation in Closed Ponds – Case Studies
- 13.9 Algae Cultivation in Closed Ponds – Q&A
- 13.10 Algae Grown in Photobioreactors
- Photobioreactors
- 14.1 Concepts
- 14.2 Types of Bioreactors Used for Algae Cultivation
- 14.3 Parts & Components
- 14.4 Design Principles
- 14.5 Costs
- 14.6 PBR Manufacturers & Suppliers
- 14.7 Photobioreactors – Q&A
- 14.8 Research Done on Bioreactors and Photobioreactors
- 14.9 Challenges in Photobioreactor
- 14.10 Photobioreactor Updates and Factoids
- 14.11 Useful Resource
- Harvesting
- 15.1 Introduction
- 15.2 Methods of Harvesting
- 15.3 Case Studies & Examples
- 15.4 Trends & Latest in Harvesting Methods
- 15.5 Challenges & Efforts
- Biodiesel from Algae
- 16.1 Introduction to Biodiesel
- 16.2 Growth of Biodiesel
- 16.3 Biodiesel from Algae
- 16.4 Why Isn’t Algal Biodiesel Currently Produced on a Large-scale?
- 16.5 Oil Yields from Algae
- 16.6 Methods to Extract Oil from Algae
- 16.7 Converting Algae Oil into Biodiesel
- Hydrogen from Algae
- 17.1 Introduction
- 17.2 Methodologies for Producing Hydrogen from Algae
- 17.3 Factoids
- 17.4 Current Methods of Hydrogen Production
- 17.5 Current & Future Uses of Hydrogen
- 17.6 Why Hasn’t The Hydrogen Economy Bloomed? – Problems with Hydrogen
- Methane from Algae
- 18.1 Introduction
- 18.2 Methods of Producing Methane from Algae
- 18.3 Methane from Algae – Other Research & Factoids
- 18.4 Traditional Methods of Methane Production
- 18.5 Methane – Current & Future Uses
- 18.6 What’s New in Methane?
- Ethanol from Algae
- 19.1 Introduction
- 19.2 Ethanol from Algae - Concepts & Methodologies
- 19.3 Efforts & Examples for Ethanol from Algae
- 19.4 Examples of Companies in Algae to Ethanol
- 19.5 Algae & Cellulosic Ethanol
- 19.6 Current Methods of Ethanol Production
- 19.7 Ethanol – Latest Technology & Methods
- Other Energy Products – Syngas, Other Hydrocarbon Fuels, Energy from Combustion
of Algae Biomass
- 20.1 Syngas and its Importance to Hydrocarbon Fuels
- 20.2 Production of Syngas
- 20.3 Products from Syngas
- 20.4 Syngas from Algae
- 20.5 Producing Other Hydrocarbon Fuels from Algae
- 20.6 Direct Combustion of the Algal Biomass to Produce Heat or Electricity
- 20.7 Trends in Thermochemical Technologies
- 20.8 Reference – Will the Future of Refineries be Biorefineries?
- 20.9 Examples of Bio-based Refinery Products
- 20.10 Reference
- Algae Meal / Cake
- 21.1 Introduction
- 21.2 Properties
- 21.3 Uses
- 21.4 Industries that Use Left-over Algae Cake
- Cost of Making Oil from Algae
- 22.1 Introduction
- 22.2 Details of Costs
- 22.3 Representative Cost of Biodiesel Production from Algae
- 22.4 Costs - Reference
- Potential for Existing Companies in Related Industries Entering Algae Energy Domain
- 23.1 Introduction
- 23.2 Industries with Synergistic Benefits from Algae Energy Opportunities
- 23.3 Case Studies
- Apex Bodies, Organizations, Universities & Experts
- 24.1 Introduction
- 24.2 Organizations
- 24.3 Universities & Research Institutes
- 24.4 Algae Energy Developments around the World
Section 2 – Processes of Algae-based CO2 Capture
Section 3 – Industry & Market Information
Section 4– Algae for Fuels
Section 5 – References
|
| Price of the Algae-based CO2 Capture | Price in USD |
| Companies /Entrepreneurs | US$ 1000 |
* People who wish to procure the report under this option are requested to send an email to muthukrishnan@eai.in with their details. Our team will get in touch with you soon |
|













