Spirulina
Omega – 3 Fatty Acids
This section provides inputs on the following aspects of omega-3 fatty acids
- Introduction
- Source of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
- Benefits and applications
- Algae Strains Used for Production
- Market Scope and Size
- Prominent Players
- Challenges
- Poly –Unsaturated Fatty Acids – Factoids
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 Fatty Acids have gained considerable importance due to their association with the prevention and treatment of several diseases like atherosclerosis, thrombosis, arthritis, cancers, etc. The omega-3 fatty acids include Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and Eicosapentaeneoic acid (EPA). The conventional source of EPA and DHA is marine fish oil, however, research studies have proved that higher amount of EPA and some DHA can be produced by the use of algae.
DHA, produced from algae, is a vegetarian source of docosahexaenoic acid, DHA. DHA is a long-chain polyunsaturated omega-3 fatty acid and is important for brain, eye and heart health throughout the lifecycle. DHA has several applications including infant formulas, products for pregnant and nursing women, food and beverage products and dietary supplements.
EPA is a polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) that acts as a precursor for prostaglandin-3 (which inhibits platelet aggregation), thromboxane-3, and leukotriene-5 groups.
Sources of Omega 3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids can be found in fish, such as salmon, tuna, and halibut, other seafood including algae and krill, some plants, and nut oils.
DHA is the primary compound of the human brain and retina. Cold-water oceanic fish oils are rich in DHA. Most of the DHA in fish and complex organisms originates in photosynthetic and heterotrophic microalgae, and becomes increasingly concentrated in organisms, as they move up the food chain. As of today DHA is commercially produced from microalgae.
EPA is obtained in the human diet by eating oily fish or fish oil— e.g., cod liver, herring, mackerel, salmon, menhaden and sardine. It is also found in human breast milk. Fish do not naturally produce EPA, but obtain it from the algae they consume. It is available to humans from some non-animal sources. Microalgae are being developed as a commercial source. EPA is not usually found in higher plants. Microalgae, and supplements derived from it, are excellent alternative sources of EPA and other fatty acids, since fish often contain toxins due to pollution.
Applications and Health Benefits of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
- Omega-3 fatty acids are highly concentrated in the brain and appear to be important for cognitive (brain memory and performance) and behavioral function. DHA specially is essential for the proper functioning of the brain and for the development of nervous system and visual abilities during the first 6 months of life.
- Omega-3 fatty acids as a part of diet help lower the risk of heart diseases.
- Omega-3 fatty acids may delay or prevent the progression of certain psychotic disorders in high-risk children and adolescents.
|
Algae Strains Producing Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Microalgae can supply omega-3 fatty acids at high concentrations. Species of Crypthecodinium, Thraustochytrium, Ulkenia and Schizochytrium are rich the omega-3 fatty acid DHA, while species of Phaeodactylum, Chlorella, Monodus, and Nannochloropsis are rich in EPA.
Crypthecodinium cohnii is a heterotrophic algal species that is currently used to produce the DHA used in many infant formulas. Research efforts have revealed that approximately 50% Thraustochytrium aureum’s total fatty acids are DHA.
Phaeodactylum tricornutum is a high EPA-producing algal species with EPA comprising 30-40% of its total fatty acids when grown using optimum culture conditions. Monodus species are photoautotrophic algae that can produce high levels of EPA, but the dependence on light results in low cell densities making them unfavorable species to use in the industrial production of EPA.
The microalga Pavlova lutheri is a potential source of economically valuable docosahexaenoic and eicosapentaenoic acids. (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15976941)
Product | Algae |
EPA | Phaedactylum tricornatum Spirulina Chlorella Nannochloropsis Monodus subterraneus |
DHA | Crypthecodinium cohnii, Schizochytrium Thraustochytrium aggregatum Ulkenia sp |
Production Process
DHA algal oil is produced via an algal fermentation process using Schizochytrium. Up to 50% of this species’ dry cell weight can comprise of fatty acids; approximately 30% of the total fatty acids are DHA. Past studies have shown that S limacinum can produce approximately four grams of DHA for every liter of media, which is higher than other species studied.
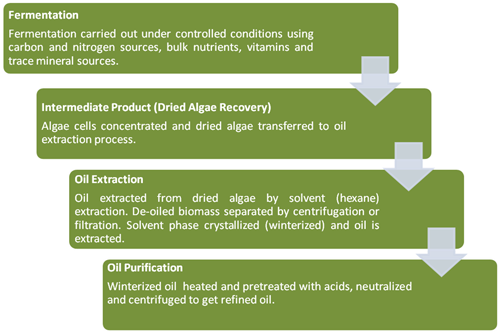
Production of DHA oil from Schizochytrium
Source: Martek Biosciences
The marine microalga Phaeodactylum tricornutum combines all the important criteria for an industrially utilizable EPA producer: rapid growth, high EPA content, photo-autotrophic production, with only sunlight as energy source and carbon dioxide as carbon source.
Researchers at the Fraunhofer Institute for Interfacial Engineering and Biotechnology (Fraunhofer IGB), Germany, grow Phaeodactylum tricornutum in a photobioreactor, the flat-panel airlift (FPA) reactor, specially developed at the Fraunhofer IGB.
Market Scope
In 2004, the global Omega-3 fatty acid market was worth US$ 690 million, and growing at about 12%. The Asian Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) ingredients market alone is expected to reach $596.6 million in 2012 (Sources: Seambiotic, Frost & Sullivan).
Today, the global market for EPA is estimated to be $300 million and that of DHA is $1.5 billion.
Global demand for Omega-3 in baby and infant food is estimated at $350 million per year. The total global market for Omega-3 for all end products estimated to be over $750 million (2006). According to market research carried out by the European market analysts Frost & Sullivan, of all the fine foods ingredients, it is Omega-3 which is expected to have the greatest future.
EPA | 300 million | 0.2 -0.5 USD/gm( Source: FAO) |
DHA | 1.5 billion | 18 – 22 USD/gm ( Source: FAO) |
Prominent Players in Omega-3 Fatty Acid Market
Company | Location |
Live Fuels | USA |
Aurora Algae | USA |
Martek Biosciences | USA |
Blue Biotech International GmBH | Germany |
Lonza | Switzerland |
Photonz | New Zealand |
Ingrepro BV | The Netherlands |
Research Efforts in Omega-3 Fatty Acids from Algae
- Researchers from the Biological Systems Engineering department of the College of Agriculture and Life Sciences in Virginia Tech have developed a novel fermentation process using microalgae to produce omega-3 fatty acids from crude glycerol, a by-product of the biodiesel industry. They then fed the omega-3 fortified algae to fish in an aquaculture facility and the fish contained significant amounts of omega-3 fatty acids.
- Fraunhofer IGB, Germany has conducted studies on the laboratory and outdoor cultivation of Phaeodactylum tricornutum and found that the EPA content is constant at 5 percent of the total dry biomass.
http://www.cals.vt.edu/news/pubs/innovations/jan2009/biodiesel.php
http://www.biodieselmagazine.com/articles/3237/glycerin-research-turns-up-new-uses
Facts
- In the early 1980s, NASA sponsored a scientific research in search of a plant-based food source that could generate oxygen and nutrition on long-duration space flights. The researchers discovered that certain species of marine algae produced rich nutrients. This research led to the development of algae-based, vegetable-like oil that contains two essential polyunsaturated fatty acids: DHA and ARA (Arachidonic acid).
- Martek Biosciences produce DHA using Cryptotheconidium cohnii for baby formula and the production was 240 tons in 2003 and the company has revenue of $300 million today.
- Martek currently owns the patents to the Schizochytrium production strain and the oil extraction process for making DHA-rich oil. Martek acquired these patents by their purchase of OmegaTech.
- The annual production of DHA in the form of oil is estimated to be 240 tons from Cryptotheconidium cohnii and 10 tons from Scizochytrium. (Source: FAO)
- As of today, USA is producing commercial scale Omega-3 fatty acids.
Related Links
|
Click Here to Know More |
|
|
Poly unsaturated fatty acids(DHA,ARA,GAL and EPA) Aquaculture Feed (Shrimp feed, Shellfish Feed, Marine Fish Larve cultivation ) |
|



